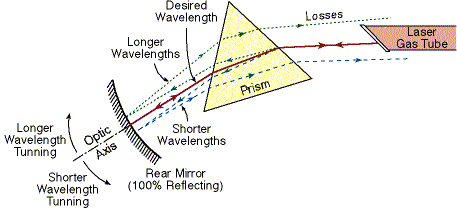

The prism is used to select the desired wavelength from the available wavelengths inside the laser.
The dispersion of the prism is the result of different index of refraction for different wavelengths.
In the visible spectrum, the index of refraction of materials is higher for shorter wavelengths.
Thus, longer wavelengths are refracted in the prism less than shorter wavelengths.
Polarization and prisms:
Ion gas lasers, such as Argon Ion, and Krypton lasers, have Brewster windows at the ends of the gas tube.
The radiation inside the cavity of a gas laser with Brewster windows at the ends is polarized. Thus, in such gas lasers it is preferred to put the prism at Brewster angle to the beam from the laser. At this Brewster angle the polarized beam suffers no added reflection losses.